Persistent poverty areas, such as rural communities in Appalachia and urban neighborhoods in the Mississippi Delta, are areas where, for more than 30 years, at least 20% of the population has lived below the federal poverty line. These areas face significant health disparities, including higher cancer rates, delayed diagnoses, and lower survival outcomes. To begin to address these issues, the NCI launched the Persistent Poverty Initiative (PPI), a $50 million investment that establishes five new Centers to build research capacity, promote cancer prevention efforts, and implement community-based programs in persistently poor census tracts. The initiative aims to address structural and institutional factors driving cancer inequities, such as income inequality, healthcare access and quality, and the built environment.
Each center is working with local communities and tribes to develop interventions that target key issues, including obesity reduction, improved nutrition, physical activity promotion, smoking cessation, and better living conditions. Additionally, the centers are training early-career investigators to conduct multilevel intervention research in underserved areas, ensuring long-term focus on reducing cancer disparities. The PPI seeks to address cancer inequities at their root causes and reduce the cancer burden across the U.S.
Persistent Poverty Initiative Awarded Sites
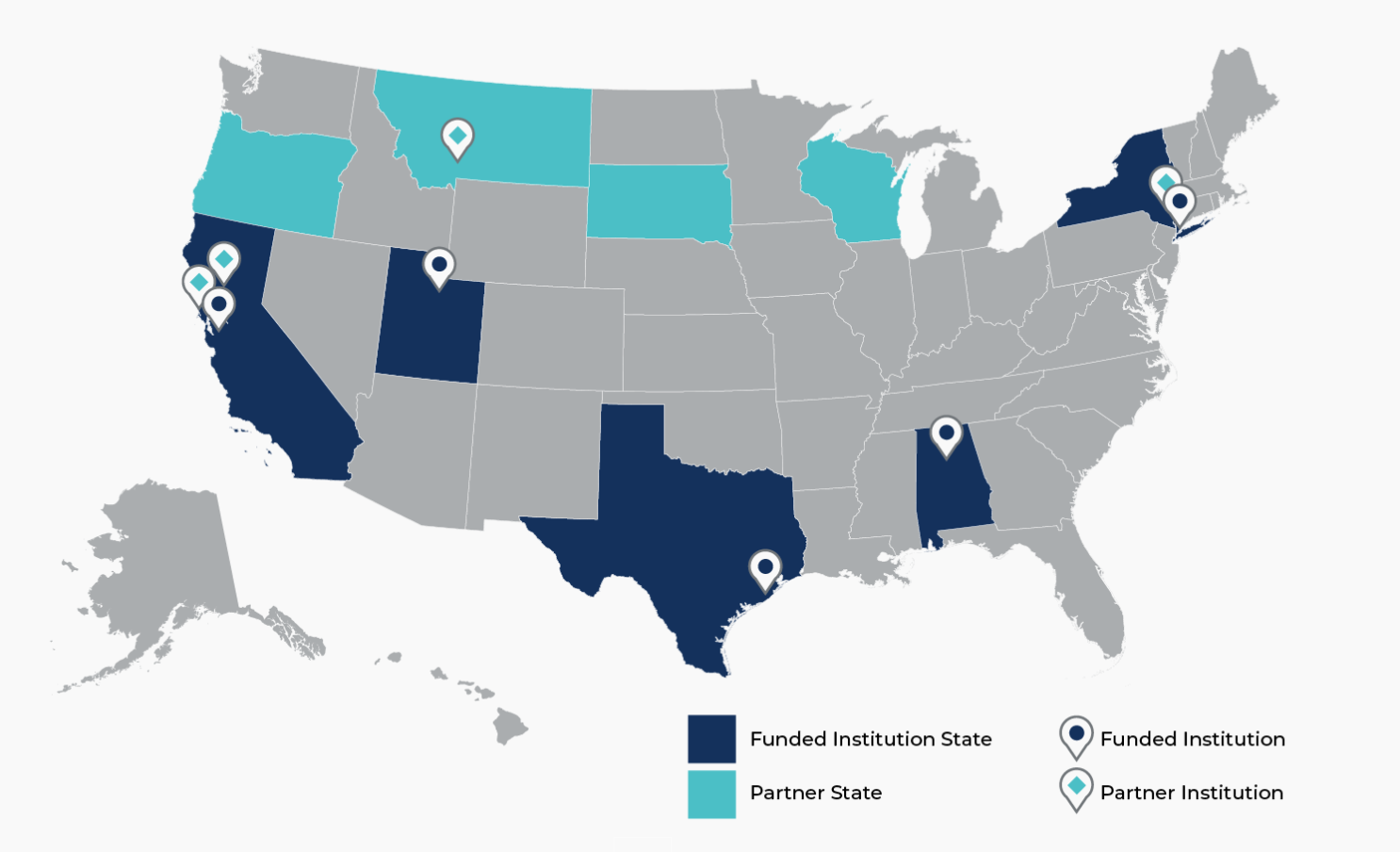
| The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center - Acres Homes Cancer Prevention Collaboration |
|---|
|
Home Page: |
| The University of Alabama at Birmingham - Cancer Awareness, Research, Engagement, & Support (CARES) Center |
|
Home Page: |
| Stanford University – Upstream Research Center |
|
Home Page: |
| Weill Medical College of Cornell University - Center for Social Capital (SoCa): Promoting Multigenerational Health |
|
Home Page: |
| The University of Utah - Center for Hope |
|
Home Page: |

